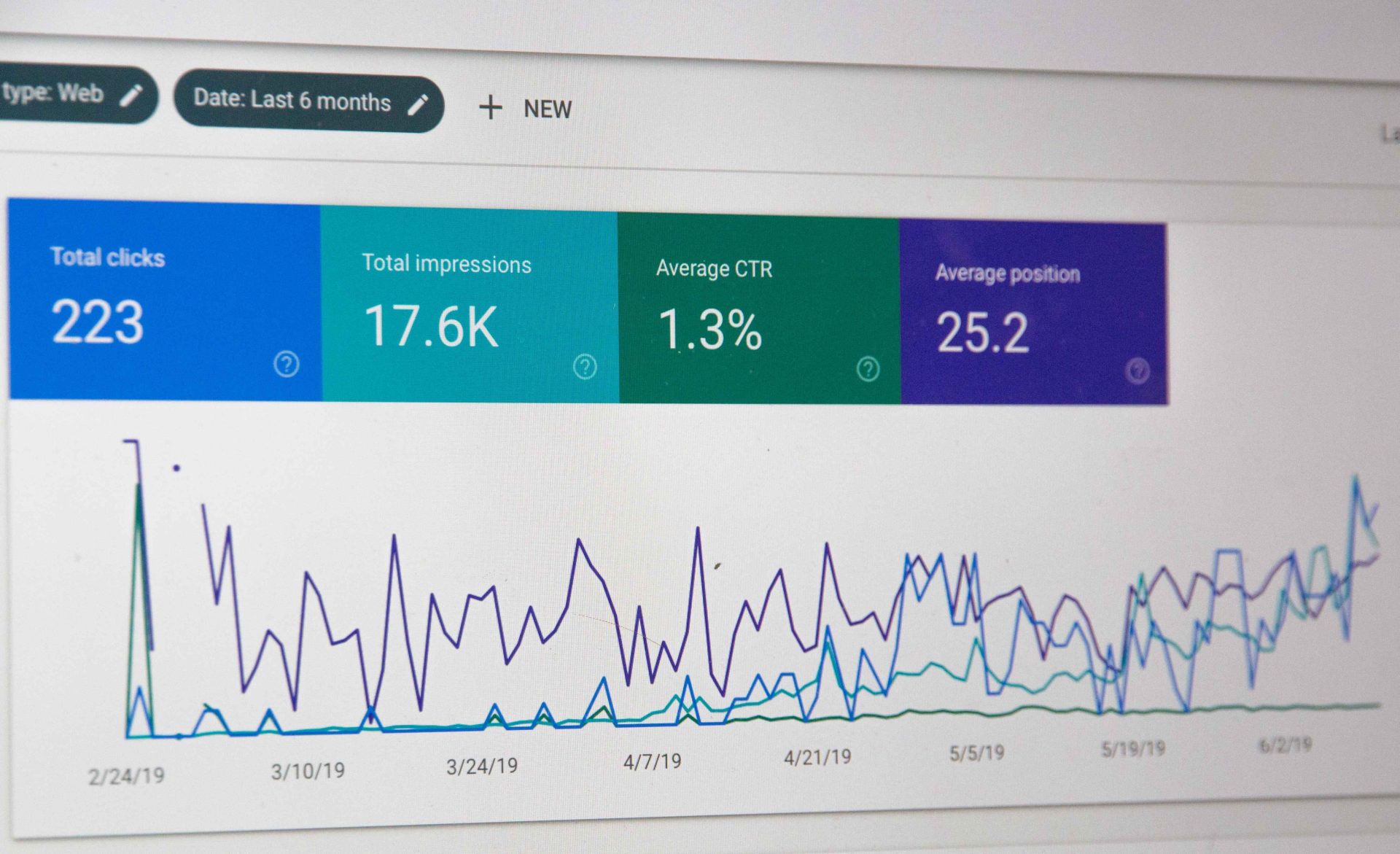
Introduction:
Google Analytics is a widely-used web analytics service that provides valuable insights into website traffic and user behavior. With the recent launch of Google Analytics 4 (GA4), marketers and analysts are curious to understand the major differences between GA4 and its predecessor, Google Analytics Universal. In this blog post, we will explore the key features and changes that differentiate GA4 from the previous version.
- User-Centric Approach:
GA4 adopts a user-centric model where events related to a single user are logged together, enabling a more holistic view of the customer journey. This shift ensures greater accuracy in measuring user interactions across multiple devices and platforms. - Event-Based Data Collection:
Unlike Universal Analytics, GA4 centers around event-based data collection instead of relying primarily on pageviews. This transition allows for a more comprehensive understanding of user engagement, including interactions such as video plays, file downloads, and form submissions. - Enhanced Machine Learning Capabilities:
GA4 harnesses the power of machine learning algorithms to provide valuable insights and automated predictions. With AI-driven features such as predictive metrics, anomalies detection, and comparative analysis, GA4 empowers marketers to make data-driven decisions more effectively. - Simplified Setup and Configuration:
Setting up GA4 is simpler compared to its predecessor. The need for manual configuration using JavaScript tags is eliminated, and instead, the implementation involves creating a new GA4 property within the Google Analytics interface. - Advanced Analysis Hub:
The new Analysis Hub in GA4 replaces the previous Analysis module in Universal Analytics, offering enhanced data exploration and visualization capabilities. Users can create custom reports with drag-and-drop dimensions and metrics, build funnels, cohort analysis, or use the built-in templates for deeper insights. - Deeper Integration with Google Ads:
With GA4, the integration between Google Analytics and Google Ads is improved and streamlined. This allows marketers to access comprehensive attribution data, compare multiple campaigns, and gain insights into how users interact with ads across different devices and channels. - Enhanced Cross-Device Tracking:
GA4 provides an improved understanding of user behavior across multiple devices and platforms. By utilizing Google Signals, marketers can leverage the power of signed-in user data to analyze cross-device user journeys and deliver personalized experiences. - Expanded Data Controls and Privacy Measures:
As privacy concerns continue to rise, GA4 offers enhanced data controls and privacy measures. Businesses can now configure data retention rules and specify how long the data is stored. Additionally, GA4 provides an option to easily handle user consent for data collection, ensuring compliance with various privacy regulations. - Emphasis on BigQuery Export:
GA4 places increased emphasis on exporting data to BigQuery, Google’s cloud-based data warehousing solution. This enables organizations to perform advanced data analysis and create custom reports by leveraging the power of BigQuery’s scalability. - Backward Compatibility and Universal Analytics Support:
Although GA4 is a new version, Google ensures backward compatibility by providing measurement ID import functionality. Additionally, GA4 supports setting up and maintaining both GA4 and Universal Analytics properties together, allowing businesses to transition gradually.
Conclusion:
With the launch of GA4, Google Analytics has undergone significant changes to meet the evolving needs of businesses in terms of user-centric tracking, advanced analytics, and improved privacy controls. The transition from Universal Analytics to GA4 offers exciting new features, including event-based data collection, advanced machine learning capabilities, and enhanced cross-device tracking. Marketers and analysts should familiarize themselves with these differences to make the most of the updated capabilities and extract valuable insights from their website data.
